Cash and other liquid assets indicate the ability to pay bills and service debt when due and remain a viable going concern. Some assets and liabilities are measured on the basis of fair value and some are measured at historical cost. Notes to financial statements provide information that is helpful in assessing the comparability of measurement bases across companies. The balance sheet distinguishes between current and non-current assets and between current and non-current liabilities unless a presentation based on liquidity provides more relevant and reliable information. Data from your balance sheet can also be combined with data from other financial statements for an even more in-depth understanding of your practice finances.
Fortunately, many places and people are willing to help you learn, including your accountant, your bookkeeper (if you employ one and don’t do the books yourself), as well as the resources at SCORE. Assets on a balance sheet are classified into current assets and non-current assets. Accountants, bookkeepers, and financial analysts create balance sheets using accounting or planning software and ERP systems. Under IFRS, property used to earn rental income or capital appreciation is considered to be an investment property.
Shareholder Equity
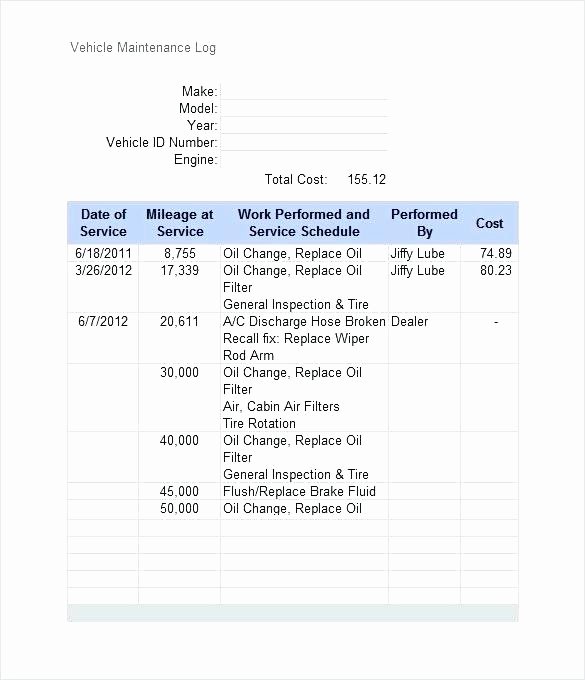
“Retained Earnings-Current” is a net profit for the period of the projections, less any owner’s draw or dividends paid . In the Fixed Assets section, the “LESS accumulated depreciation” figure is the total of all depreciation accrued over the years on all fixed assets still owned by the company. Be sure to enter it as a negative number so the spreadsheet will subtract it from Total Fixed Assets. For the sake of this example, let’s The Balance Sheet ignore any cash you’ve paid toward your loan and keep the liability value at $300,000. The debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) indicates the relative proportion of shareholder’s equity and debt used to finance a company’s assets. Inventory management is to identify the level of inventory which allows for uninterrupted production but reduces the investment in raw materials – and minimizes reordering costs – and hence, increases cash flow.
- Cash management involves identifying the cash balance which allows for the business to meet day-to-day expenses, but reduces cash holding costs.
- Owners’ equity, also known as shareholders’ equity, typically refers to anything that belongs to the owners of a business after any liabilities are accounted for.
- Small business owners sometimes prepare personal financial statements, including a balance sheet, to get financing.
- The balance sheet contains statements of assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
- Potential investors analyze a company’s performance by examining what a business owns versus what it owes.
- A balance sheet is a snapshot in time rather than a representation of long-term fiscal trends.
- These accounts vary widely by industry, and the same terms can have different implications depending on the nature of the business.
It may not provide a full snapshot of the financial health of a company without data from other financial statements. Business owners use these financial ratios to assess the profitability, solvency, liquidity, and turnover of a company and establish ways to improve the financial health of the company. Using financial ratios in analyzing a balance sheet, like the debt-to-equity ratio, can produce a good sense of the financial condition of the company and its operational efficiency.
Read our comprehensive guide to ACH Payments
IFRS provide companies with the choice to report an investment property using either a historical cost model or a fair value model. Trade receivables, also referred to as accounts receivable, are amounts owed to a company by its customers for products and services already delivered. The balance sheet is also known as the statement of financial position. Although the balance sheet represents a moment frozen in time, most balance sheets will also include data from the previous year to facilitate comparison and see how your practice is doing over time. Finally, total assets are tabulated at the bottom of the assets section of the balance sheet. If a company is public, public accountants must look over balance sheets and perform external audits.
- A company’s assets must equal their liabilities plus shareholders’ equity.
- IFRS provide companies with the choice to report PPE using either a historical cost model or a revaluation model.
- Accounting systems or depreciation methods may allow managers to change things on balance sheets.
- In both cases, the external party wants to assess the financial health of a company, the creditworthiness of the business, and whether the company will be able to repay its short-term debts.
- The debt to equity ratio measures financial leverage and demonstrates what proportion of organizational debt versus organizational net assets are being utilized to support the organization’s finances.
A company’s balance sheet, also known as a “statement of financial position,” reveals the firm’s assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity . https://quick-bookkeeping.net/, together with the income statement and cash flow statement, make up the cornerstone of any company’s financial statements. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of information that is linked to both the cash flow and income statements. For example, the cash balance that appears on the balance sheet is the ending balance used in the cash flow statement.
Current (Short-Term) Liabilities
You can learn this by looking at the different accounts and their values under assets and liabilities. You can also see that the assets and liabilities are further classified into smaller categories of accounts. The value of balance sheet accounts can be used to calculate ratios that show the liquidity, efficiency and financial structure of a business.
- The ownership percentage depends on the number of shares they hold against the company’s total shares.
- A balance sheet is also different from an income statement in several ways, most notably the time frame it covers and the items included.
- Working capital is a financial metric which represents operating liquidity available to a business, organization or other entity, including a governmental entity.
- She is experienced at transforming complex concepts into easily digestible articles to help anyone better understand the world we live in.
Long-term liabilities are any debts that must be repaid by your business more than one year from the date of the balance sheet. This may include start up financing from relatives, banks, finance companies, or others. Current assets most commonly used by small businesses are cash, accounts receivable, inventory and prepaid expenses. Balance sheet substantiation is an important process that is typically carried out on a monthly, quarterly and year-end basis.



